Free eye tracking software programs offer accessibility and affordability, allowing users to gather gaze data. Pros include cost-effectiveness and ease of use. However, the cons involve limited features and less accuracy compared to high-end commercial alternatives.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Eye tracking technology is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the field of market research, psychology, and human-computer interaction. The recent development of both commercial and free eye-tracking software has democratized its use and made it more accessible to researchers and businesses alike.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 free eye-tracking software available and their features. We will discuss the benefits and limitations of using free eye tracking software. By the end of this article, readers will have a better understanding of the capabilities of free eye-tracking software and how to incorporate it into their research and business practices.
Researchers have attempted to track the eye movements for well over a century. By knowing what is being looked at, it’s possible to understand what is driving visual attention.
This has been important for psychologists and other human behavior researchers, and has become increasingly used by people working in other related fields, such as neuromarketing.
As time has passed, the technology and software have improved as well. This has formed the eye tracking field of today, in which incisive discoveries are more accessible than ever through the use of advanced eye tracking software.

iMotions Lab
Powering Human Insights
The world’s leading human behavior research software for eye tracking, facial expression analysis, GSR, EEG and more
There are various options available for eye tracking, and some of these are offered free-of-charge. While this can be a great benefit for many users, this advantage is dependent on the software working well – if it doesn’t function as hoped, or offer the capabilities required, then the price doesn’t matter. Below, we outline the pros and cons of free eye tracking software and discuss the benefits of using a more advanced platform like iMotions for your research.
Capability Rundown of Free Online Eye Trackers
While this list features 10 eye tracking software programs, we also (quite literally) looked at several others. Those that have been left off the list include deprecated or non-functional programs, as well as those that are not truly free.
Below we have listed 10 eye tracking software programs, showing whether or not certain functions exist, and their accessibility.
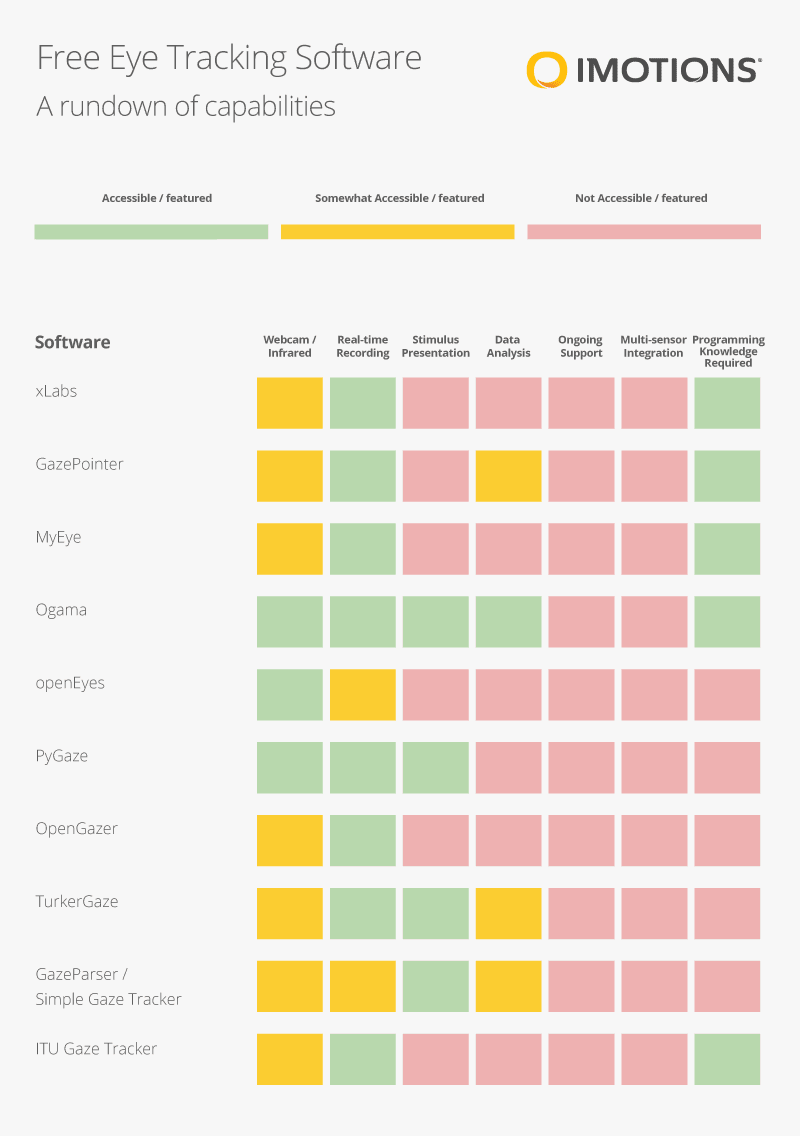
The list above captures the essentials of the free eye tracking software that we have elucidated further below.
Top 10 Free Eye Tracking Software
xLabs – Discontinued
Built as a browser extension for Google Chrome, this startup is the result of 2 years R&D by the four co-founders. You can install the software directly into your browser here. xLabs has also led to a spinoff, EyesDecide that provides testing of stimuli through their webcam-based eye tracking.
 Pros
Pros
+ Very easy to install
+ Easy to use
+ Works in multiple platforms
 Cons
Cons
– Only works with webcams (decreased accuracy)
– Doesn’t allow integrated stimulus presentation
– No simple way to obtain the data
– No data analysis options
– No support
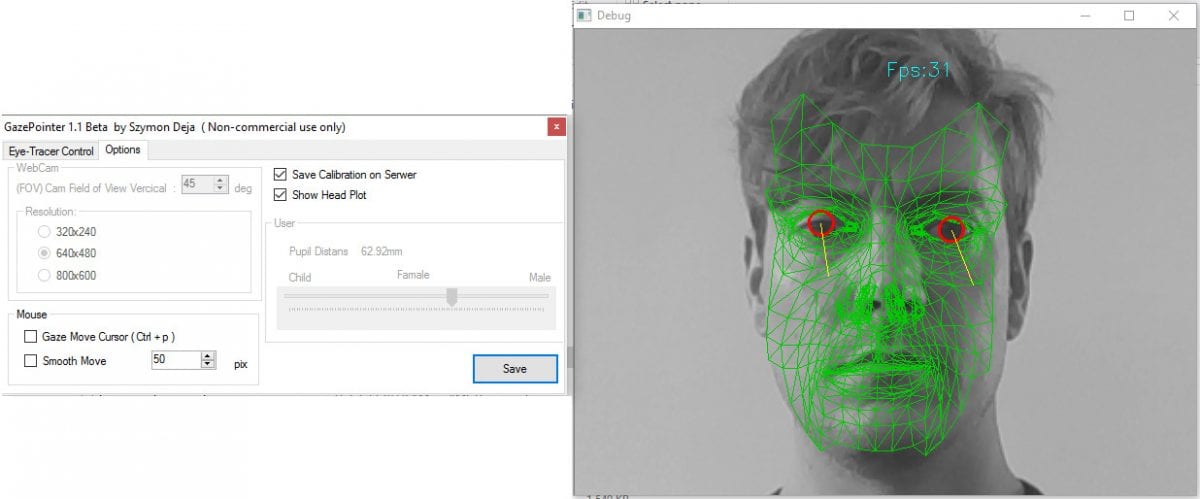
GazePointer
The GazePointer program is straightforward to install, and runs on Windows, making it one of the more widely accessible programs on this list.
 Pros
Pros
+ Easy to install
 Cons
Cons
– Only works with webcams (decreased accuracy)
– Doesn’t allow integrated stimulus presentation
– No support
– No data analysis options
MyEye
MyEye has been designed for use by people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a neuromuscular disease. It is in the Beta phase of development.
 Pros
Pros
+ Easy to install
 Cons
Cons
– No support or even documentation
– Doesn’t allow integrated stimulus presentation
– No data analysis options
– No simple way to obtain the data
Ogama
Ogama is open source software developed at the Free University of Berlin.
 Pros
Pros
+ Allows basic stimulus presentation
+ Provides basic data analysis options
 Cons
Cons
– No support
– No updates in over three years
openEyes
This open source software allows eye tracking from both infrared and visible spectrum illumination, using Matlab.
 Pros
Pros
+ Can be used with webcams and infrared eye trackers
 Cons
Cons
– Requires Matlab (commercial software) and working knowledge of Matlab
– Doesn’t allow integrated stimulus presentation
– No support
– No data analysis options
PyGaze
This software runs in Python, and was published by three researchers (from Oxford University, Aix-Marseille University, and Utrecht University) in 2014.
 Pros
Pros
+ Stimulus presentation (requires knowledge of Python)
+ Data analysis (requires knowledge of Python)
 Cons
Cons
– Requires a good working knowledge of Python
– Not much support
OpenGazer
OpenGazer was designed 8 years ago to increase the accessibility of computer use, and was originally supported by Samsung and the Gatsby Charitable Foundation.
 Pros
Pros
+ Potentially compatible with Apple OS (although requires programming knowledge)
 Cons
Cons
– Only works with webcams (decreased accuracy)
– Requires Linux (and knowledge of how to use Linux)
– No support
TurkerGaze
TurkerGaze is a software program developed by researchers at Princeton. The system runs in Linux and is dependent on several other Linux programs to function.
 Pros
Pros
+ Provides basic data analysis options
 Cons
Cons
– Best used with a head restraint
– Requires Linux (and knowledge of how to use Linux)
GazeParser / Simple Gaze Tracker
This software consists of two components: GazeParser (for stimulus presentation, data conversion, and analysis), and SimpleGazeTracker is (used for gaze recording) with the use of Python.
 Pros
Pros
+ Can perform stimulus presentation and data analysis (although requires knowledge of Python)
+ Provides basic data analysis options (with use of Python coding)
 Cons
Cons
– Requires a motion capture or machine vision camera
– Requires a chinstrap / head restraint to restrict head movement
– Requires a good working knowledge of Python
ITU Gaze Tracker
Originally developed by the Gaze Group at the University of Copenhagen, ITU Gaze Tracker is an open-source platform designed to increase the accessibility of technology.
 Pros
Pros
+ Easy to install
 Cons
Cons
– Requires building own infrared eye tracker (if not using webcam)
– No support
The Verdict
While the free eye tracking software can be a fun experiment – and the feats they pull off are sometimes still impressive (particularly when constructed by small teams) – none are able to meet the requirements of eye tracking for work and research. Making discoveries, and uncovering results, requires that eye tracking is accurate, both in space and time.
It is due to these drawbacks that eye tracking software requires a certain amount of credibility – getting past peer-review to publish research will be an even more difficult process if the software itself isn’t widely recognized as leading to legitimate results. –
There is – as always – the potential for things to go wrong, and if you encounter any problems while figuring the software out, it’s unlikely that you will receive much support. As many of the programs have been created by individuals or small groups, chances are that they won’t have the time to help users or fix inevitable software bugs.
There are even more things to consider – are there any stimulus presentation options? Can it be integrated with other software, such as PsychoPy, E-Prime, or even in-browser presentation? How is the fixation algorithm constructed? Is the data analyzable, or even accessible? –

This could also mean understanding the source code to provide explanations about its use. For a programmer this could be relatively straightforward, but will likely involve a level of expertise well above the average for most people working with eye tracking.
For most of the software, the features are rarely fitted to the ideal situation.
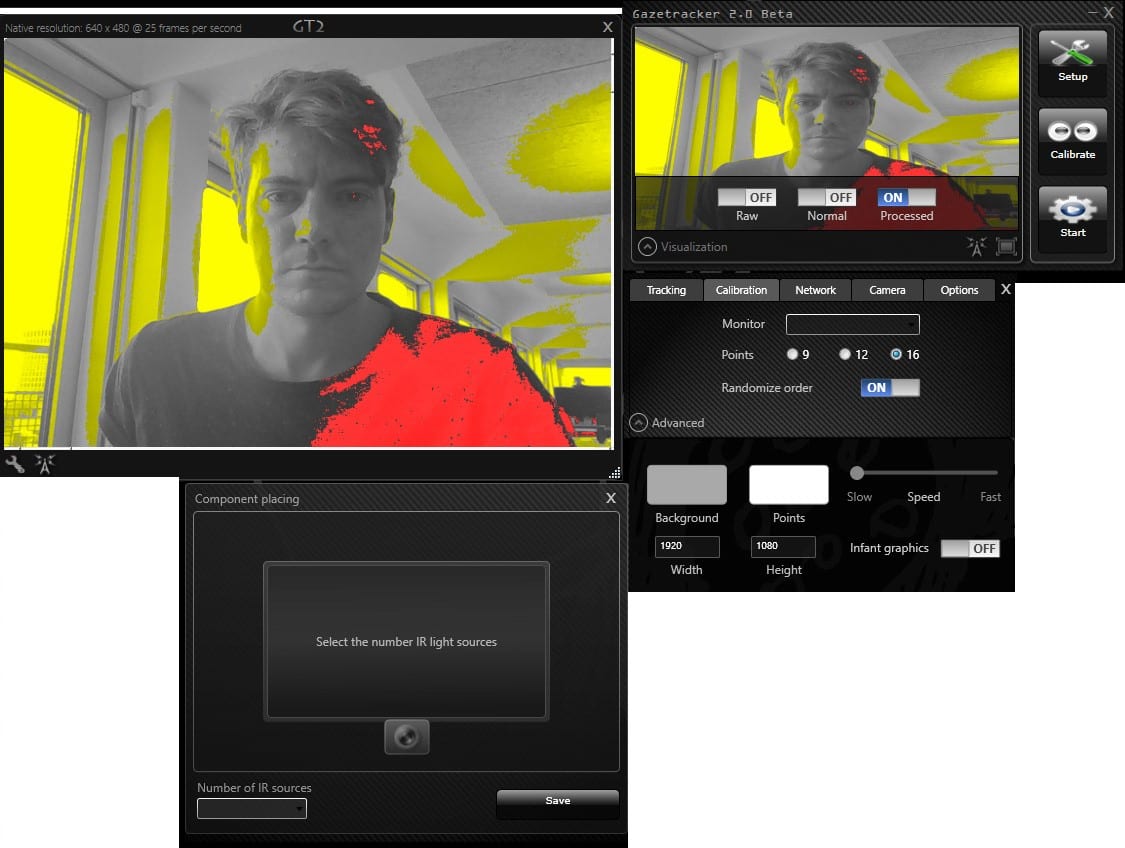
Free webcam-based eye tracking software?
Many of the free eye tracking software offerings above only incorporate data from webcams and provide limited data analysis capabilities. This, of course, promises more accessibility to the user, yet will not be able to deliver the same level of accuracy as infrared eye trackers. In spite of significant advances in the field of webcam eye tracking, they are still not “research grade” if you will. This limitation can easily be acceptable for researchers and data collectors who are, for example, interested in recruiting many respondents across global locations, for studies where a significant amount of participants are needed, or if they need to distribute studies remotely due to physical limitations, travel restrictions, etc.–
Choosing which software to use also comes down to trust. If you’re planning on using the software for research, then you need to be able to defend its use to the research community – this isn’t difficult with companies that have already built trust through years of work and communication but will unavoidably be more difficult with small startup operations.
Why iMotions is the Best Eye Tracking Online Software?
Highly Accurate Eye-Tracking Data for Research
The guiding principle of iMotions’ development efforts has always been to produce research-grade software. That means that we will not release anything that we do not believe could be used to conduct high-end eye tracking research.
What sets iMotions Webcam-based Eye Tracking apart from other webcam-based systems is its exceptional accuracy and ease of use. Leveraging our advanced computer vision algorithm WebET 3.0, the system extracts precise gaze data from ordinary webcams, minimizing setup time and ensuring consistent data quality.
From marketing professionals seeking insights into consumer attention to educators analyzing online learning behaviors, iMotions empowers researchers with a tool that combines unparalleled accuracy, user-friendliness, and accessibility.
Multiple Valuable Options
iMotions offers two valuable solutions for eye tracking: our desktop application iMotions Lab and our web application iMotions Online. The desktop solution allows you to synchronize and analyze data from infrared eye trackers as well as online data collection via webcams. iMotions Online is completely browser-based and allows for webcam-based eye tracking and facial expression analysis. Both come with the possibility for robust visualizations, annotations, and metrics exports that are integral to high-quality eye tracking research.
Carrying out research and work with eye tracking in iMotions is both simple and comprehensive. A whole range of features is readily available, allowing you to carry out advanced research in a plug-and-play solution. Some of the features are listed below.
Features and metrics breakdown
- Integration with 20+ eye tracking models from a range of vendors such as Pupil Labs, EyeTech, Smart Eye, Eye Tribe, GazePoint, etc – including screen-based, eye tracking glasses, and webcams
- Simple installation and setup
- Intuitive user interface
- Presentation of screen-based multimedia stimuli (images, videos, websites, games, software interfaces and 3D environments)
- Compatible with mobile devices / external interfaces
- Real-world recording with glasses or remote eye trackers
- Ability to expand use with API
- Integrated study setup and design
- Integrated data quality assurance tools
- Static & dynamic areas of interest (AOIs), manual and semi-automated options
- Individual & aggregate gaze replays
- Automated AOI generation allows for tracking of an area throughout a video
- Automated metrics such as Time to First Fixation (TTFF), time spent, ratio, revisits, fixation count, mouse clicks, keystrokes etc.
- Real-time recording
- Static & dynamic heatmaps
- Create live and post markers
- Raw data including X,Y coordinates of eye position, pupil size, & distance to the screen
- Well validated in hundreds of publications
- Continuous support
- Seamless synchronization with other biosensors, such as facial expression analysis, EEG, GSR, ECG, EMG, and more
Expanding human behavior research methods to include other sensors will mean more data, and ultimately more incisive findings. iMotions is not only the research platform that is designed (and continually updated) for this purpose – it also includes an easy-to-use setup with a vast array of accurate eye tracking features.
While the price tag – or rather lack of price tag – can be an attractive aspect, if the tracking is slow or inaccurate then little can be done. Accuracy and reliability are necessary when it comes to creating a deeper understanding of human behavior – and that’s difficult to put a price on.
I hope you’ve enjoyed reading about the advantages and disadvantages of free eye tracking software. To learn more about how iMotions can help you carry out flawless eye tracking experiments, and to see which advanced features are available, get in touch and schedule a demo.
Eye Tracking
The Complete Pocket Guide
- 32 pages of comprehensive eye tracking material
- Valuable eye tracking research insights (with examples)
- Learn how to take your research to the next level

Note: this article was originally published in 2019 and has been updated in 2021 and 2023 to include the new Online Data Collection module as well as iMotions Online.
iMotions Software Products
Full-scale human behavior
research solutions
A software research suite that integrates an ecosystem of virtually any biosensor technology to provide the most robust data and insights available.