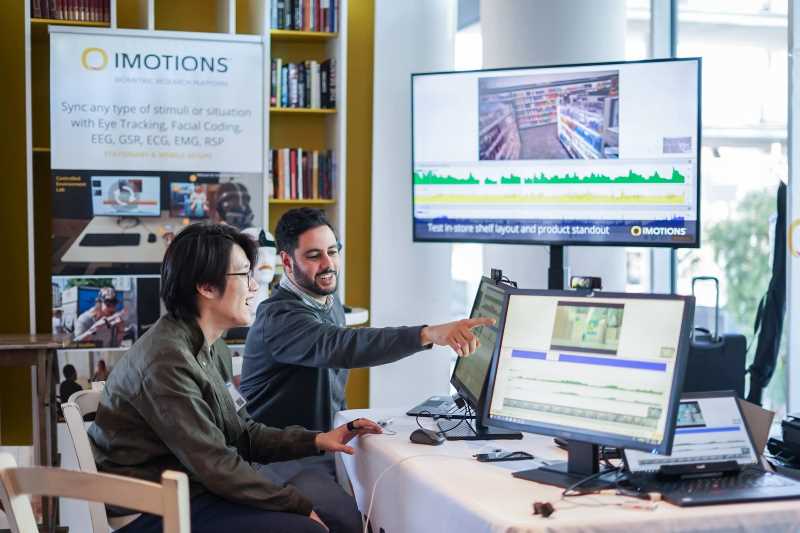
Abstract
This project looks at how people approach collaborative interactions with humans and virtual humans, particularly when encountering ambiguous or unexpected situations. The aim is to create natural and accurate models of users’ behaviors, incorporating social signals and indicators of psychological and physiological states (such as eye movements, galvanic skin response, facial expression and subjective perceptions of an interlocutor) under different conditions, with varying patterns of feedback. The findings from this study will allow artificial agents to be trained to understand characteristic human behaviour exhibited during communication, and how to respond to specific non-verbal cues and biometric feedback with appropriately human-like behaviour. Continuous monitoring of “success” during communication, rather than simply at the end, allows for a more fluid and agile interaction, ultimately reducing the likelihood of critical failure.
Related Posts
-
Multiface Analysis in Action: Advanced Methods for Studying Facial Expressions in Group Settings
-
Memory and Visual Attention: 5 Foundational Eye-Tracking Experiments
-

Converting Raw Eye-Tracking Data into Cognitive Load Indicators
-

Desire Before Delight: Why Wanting Drives Consumer Choice More Than Liking































