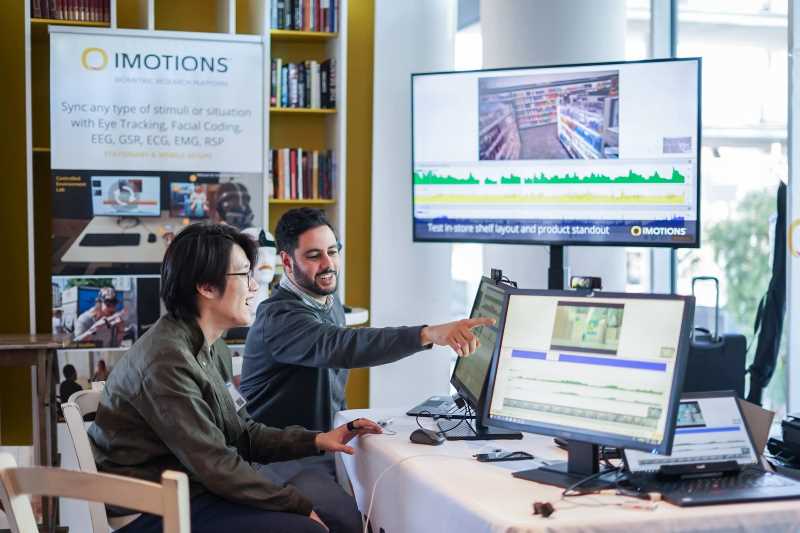
In the era of Industry 4.0, the importance of human-robot collaboration (HRC) in the advancement of modern manufacturing and automation is paramount. Understanding the intricate physiological responses of the operator when they interact with a cobot is essential, especially during programming tasks. To this aim, wearable sensors have become vital for real-time monitoring of worker well-being, stress, and cognitive load. This article presents an innovative dataset (SenseCobot) of physiological signals recorded during several collaborative robotics programming tasks. This dataset includes various measures like ElectroCardioGram (ECG), Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), ElectroDermal Activity (EDA), body temperature, accelerometer, ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG), Blood Volume Pulse (BVP), emotions and subjective responses from NASA-TLX questionnaires for a total of 21 participants. By sharing dataset details, collection methods, and task designs, this article aims to drive research in HRC advancing understanding of the User eXperience (UX) and fostering efficient, intuitive robotic systems. This could promote safer and more productive HRC amid technological shifts and help decipher intricate physiological signals in different scenarios.
Related Posts
-
Multiface Analysis in Action: Advanced Methods for Studying Facial Expressions in Group Settings
-
Memory and Visual Attention: 5 Foundational Eye-Tracking Experiments
-

Measuring Consumer Happiness: How Biometrics Can Help Assess What Products Make People Feel Good
-

Desire Before Delight: Why Wanting Drives Consumer Choice More Than Liking































