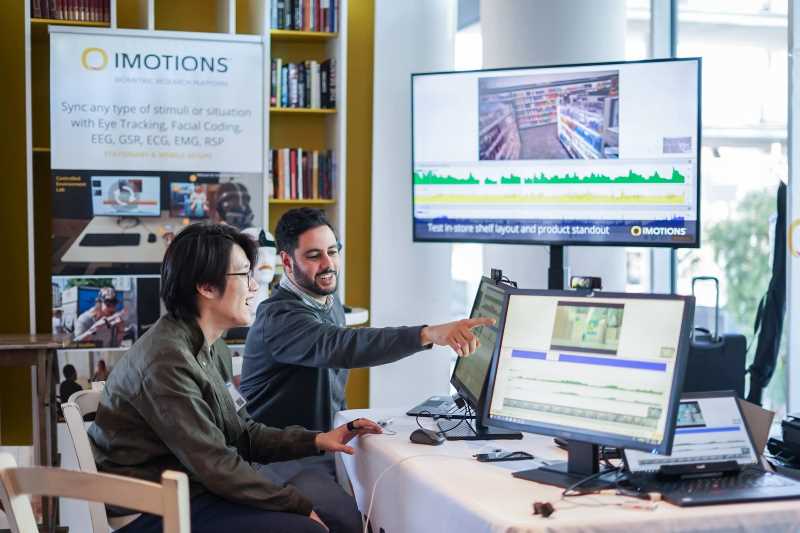
Abstract: The goal of this study was to examine college students’ (n = 61) contextualized emotions during in-game actions while playing CRYSTAL ISLAND, a game-based learning environment where students are tasked with solving the mystery of what illness impacted all island inhabitants. We examined emotions during in-game actions: during book reading, after scanning food items for the transmission source, and after submitting a final diagnosis. We dichotomized each activity’s feedback into a positive or negative outcome: a relevant or irrelevant book for solving the mystery, testing food items that generate a positive or negative result, or submitting a correct or incorrect final diagnosis. Results revealed that expressing joy while reading a relevant book and expressing confusion after a positive scan significantly positively predicted overall game score, which we used as a proxy for problem-solving performance. Implications include understanding different levels of emotions students express during learning with all advanced learning technologies.