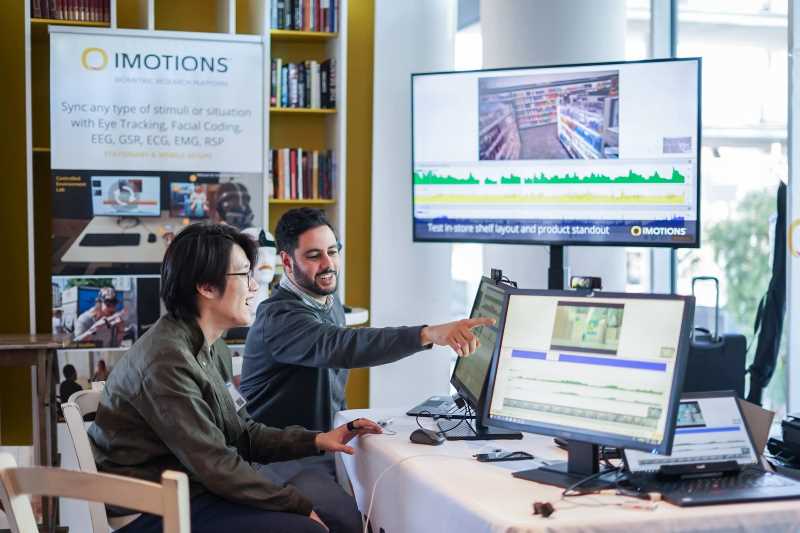
Understanding human responses to the built environment is vital for effective urban design and sustainable transportation planning. This study presents a methodology that employs eye-tracking technology and facial expression analysis to compare conscious and unconscious reactions to street designs featuring differing levels of Green and Complete Street (GCS) elements. Conducted in Devens, Massachusetts, the research evaluates the impacts of current and prospective design modifications on human well-being. The study employed still images and videos of urban streetscapes, altered to reflect no, low, and high GCS levels. Unconscious reactions were recorded via remote eye-tracking and emotion recognition software, while conscious responses were gathered using an emoji-based self-report survey. High-GCS environments elicited stronger visual attention and more positive emotions, especially toward green infrastructure. The results highlight the importance of incorporating pedestrian-friendly, green elements into urban design.