Eye tracking enables recording of eye position and movement based on optical tracking of corneal reflections, thereby making the analysis of eye movements and gaze positions in both 2D- and 3D-environments possible. It helps to analyze human processing of visual information for interactive and diagnostic applications.
Early eye trackers were huge and cumbersome – eye trackers today can be as tiny as a pencil case, greatly expanding the possible use cases for a more flexible device. Any domain in research can highly benefit from the collection of quantitative evidence with a method that doesn’t make participants uncomfortable.
Eye tracking measures attention, interest, and arousal, making it a great tool for any kind of human behavior research applied in a variety of fields such as Psychology, Medicine, Marketing, Engineering, Education, and Gaming as well as for enhancing human computer interaction by using the eyes for navigation and controls.
The following 8 eye tracking applications are the most commonly utilized:
1. Academic and Scientific Research
Without a doubt, the academic and scientific research fields are currently making the most out of eye tracking for cognitive, developmental, experimental and media applications in psychology and neuroscience.
2. Market Research
During the past few years, eye tracking for market research has become increasingly important. Many leading brands use the tool to evaluate their products, designs, advertising or even the shopping behavior of their customers to optimize the overall customer experience.
With eye tracking, it is possible to measure attention to brands, products, and their key messages as well as the ease or difficulty of store navigation.

3. Psychology Research
Within this area, visual attention can be measured and correlated with other measures such as how the brain works. The visual attention research can be done for normal populations as well as for specific subpopulations that have conspicuous behavioral patterns or different kinds of mental health disorders.
4. Medical Research
Eye tracking in combination with conventional research methods or other biosensors can even be helpful for diagnosing diseases such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Schizophrenia, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease.
For instance, it can be used to detect drowsiness or support various other fields for medical, quality assurance or monitoring use.
5. Usability Research
Eye tracking for usability and user experience is an emerging field using these methodologies. One classic example is website testing. Here, attention to real estate, communication, and call to action (CTA) can be measured.
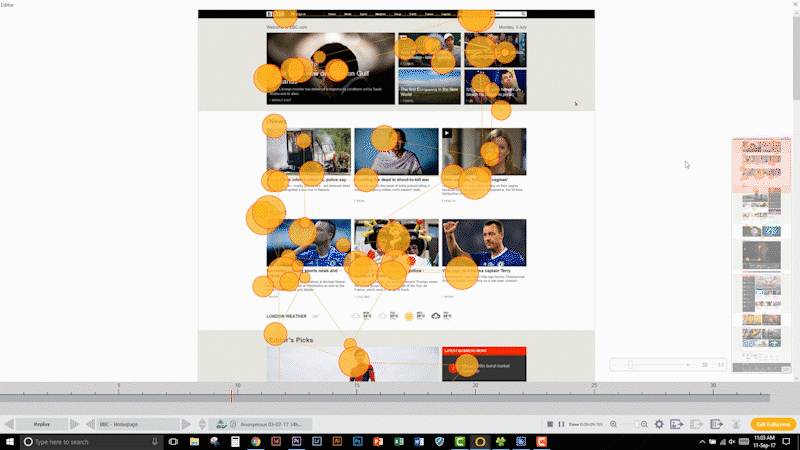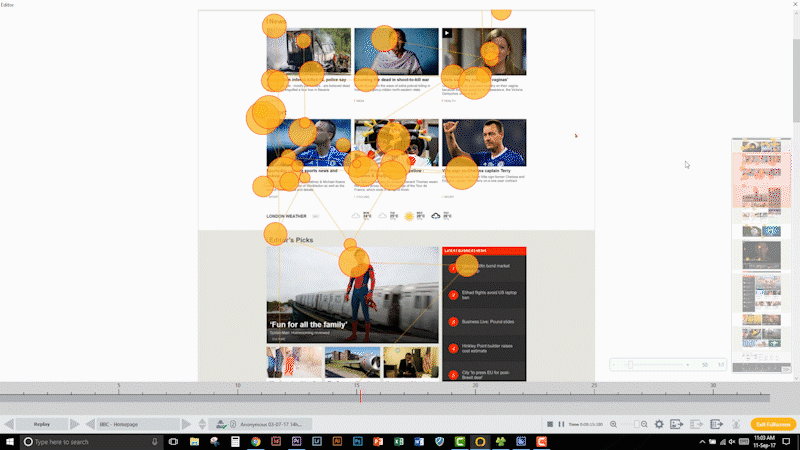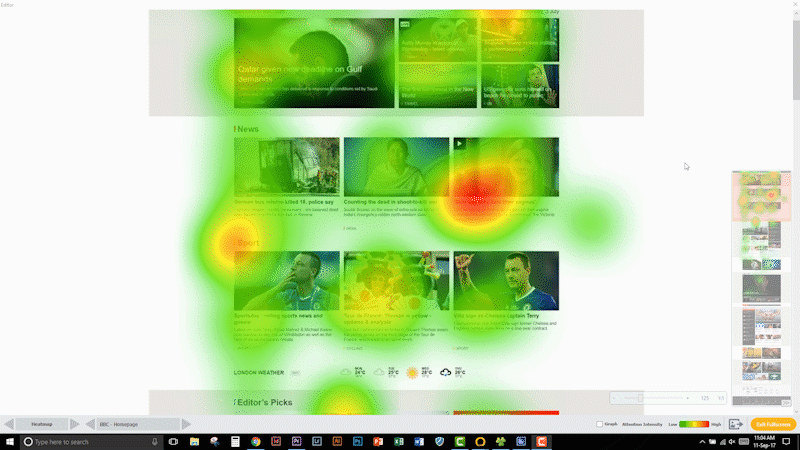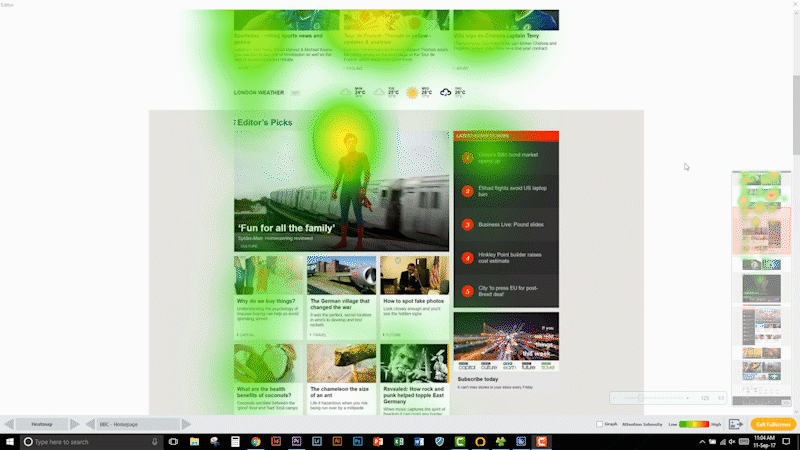
If it is difficult to find a certain product on a website, the owner of that website is very likely losing out on revenue. So, if that website could be improved to increase the findability of a product, a fast and big return on investment can be seen. Similar applications can be applied to mobile apps on tablets and smartphones.
If it is difficult to find a certain product on a website, the owner of that website is very likely losing out on revenue. So, if that website could be improved to increase the findability of a product, a fast and big return on investment can be seen. Similar applications can be applied to mobile apps on tablets and smartphones.
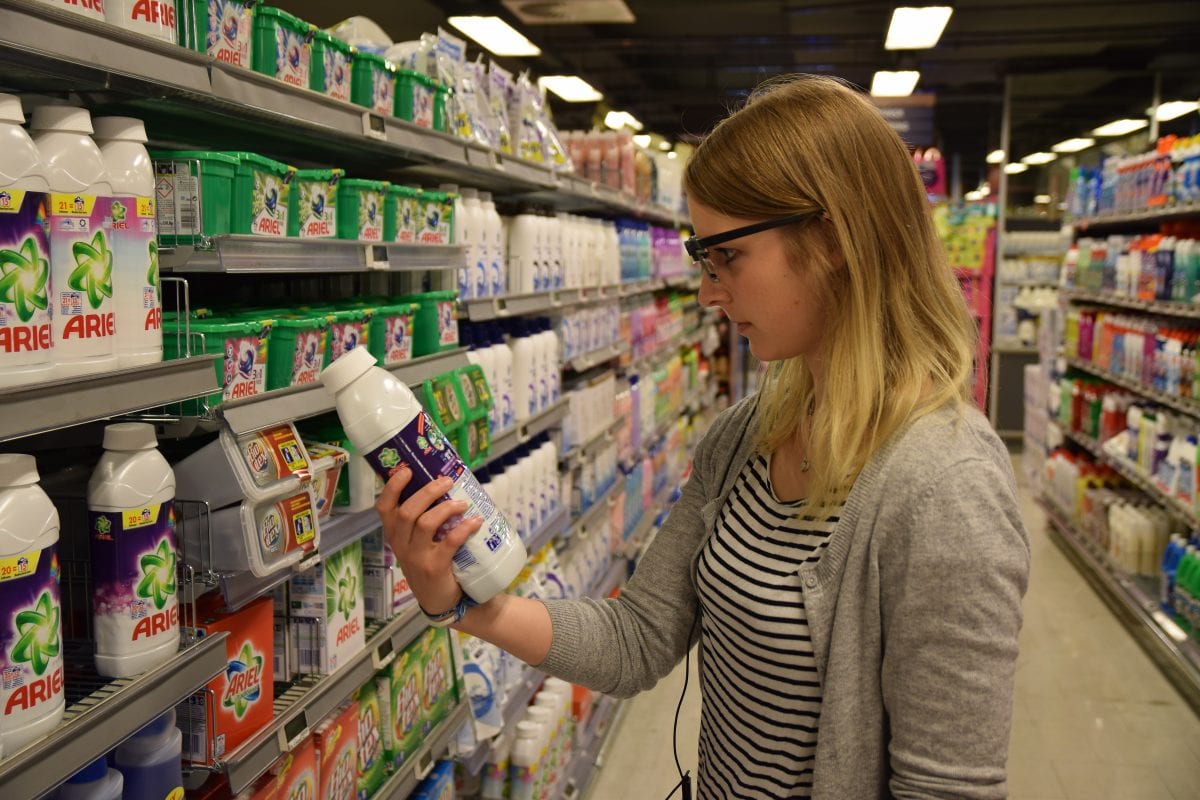
6. Packaging Research
Generally, there is a lot of money invested into designing packages of a product before they go to market. This is the case especially for fast moving consumer goods because the competition is very fierce.
It is necessary to make sure that the package of a product gets enough visual attention on the shelves, meaning it has to stand out from the others. Eye tracking is basically used here for designing the packages and understanding the customers’ preferences.

7. PC and Gaming Research
Eye tracking has also been introduced to the human-computer interaction and gaming industry which now enables for instance game designers to get a better understanding of the game experience so that it is somewhat possible to control the experience and create features that push the boundaries of reality even more.
In the time to come, it will most likely even be possible to personalize the game’s development in regard to pupil dilation of the player and the gamer will be able to control the game with eye movements.
8. Human Factors and Simulation
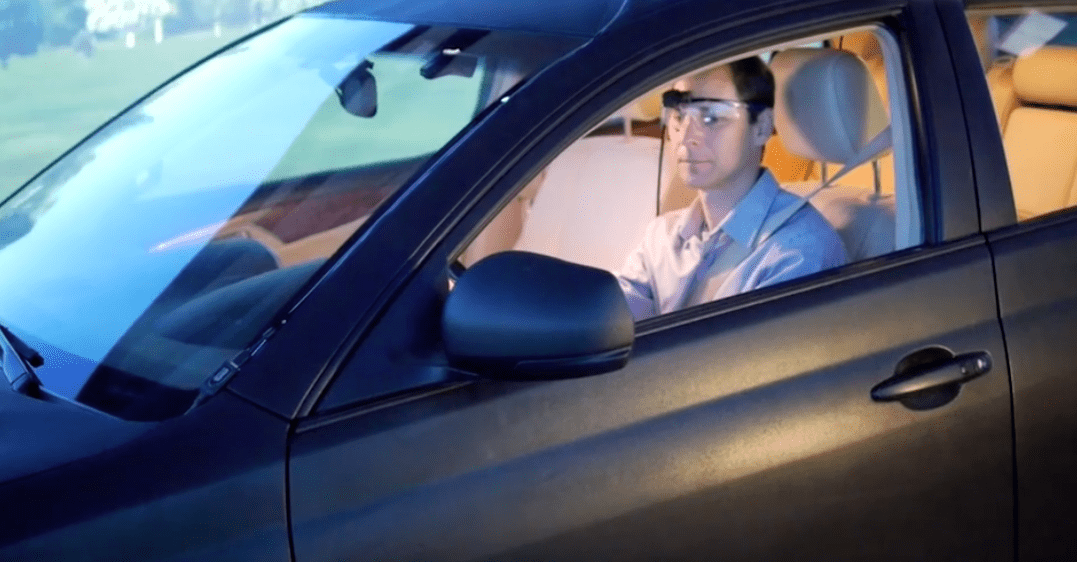
Automotive research has embraced eye tracking glasses for a long time to gauge driver’s visual attention – both with respect to navigation and layout of dashboards. In the near future automobiles might be able to be responsive towards their driver’s eye gaze, eye movements or the dilation of the pupil.
The applications mentioned above are only the most commonly used within eye tracking research. Eye tracking is however not limited to these and can in combination with further biometric sensors be even more powerful.

If you have further questions regarding eye tracking, its usage, possible applications, or what eye tracking can do for you, please contact the team at iMotions.