Human factors is the study of how people interact with systems, environments, and technology to improve safety, efficiency, and usability. It applies to aviation, healthcare, UX design, and workplace safety, minimizing errors and optimizing performance through ergonomics, cognitive psychology, and human-centered design. Learn its importance, principles, and real-world applications.
Table of Contents
Human Factors plays a crucial role in various industries, from healthcare and aviation to product design. Understanding the significance of Human Factors is essential in enhancing performance, safety, usability, and overall user experience. By delving into the definition and overview of Human Factors, exploring its vital role in different industries, examining key principles, tackling challenges, and discussing future trends, we can gain valuable insights into this fascinating field.
Understanding the Concept of Human Factors
Definition and Overview of Human Factors
Human Factors, often referred to as ergonomics, involves the study of the interplay between humans, machines, and their surrounding environment. It focuses on optimizing the design, function, and interaction of systems to ensure efficiency, comfort, and safety for users. By considering human capabilities, limitations, and behaviors, Human Factors aims to improve performance, minimize errors, and enhance user satisfaction.
When it comes to understanding the concept of Human Factors, it is important to delve deeper into the various aspects that it encompasses. One key aspect is the consideration of anthropometry, which involves the measurement of human body dimensions. By understanding the range of body sizes and shapes, designers can create products and systems that accommodate the needs of a diverse user population.
Another crucial aspect of Human Factors is the study of human cognition. This involves examining how people perceive, process, and interpret information. By understanding the cognitive processes involved in using a system or product, designers can optimize its usability and ensure that users can easily understand and navigate through it.
The Importance of Studying Human Factors
Studying Human Factors is crucial as it directly impacts the success and well-being of users. By understanding how humans interact with technology and their environment, we can enhance safety, productivity, and user experience. Human Factors research provides valuable insights into human cognition, physical abilities, and psychological factors, contributing to the development of user-friendly systems and products.
One area where the importance of studying Human Factors becomes evident is in the field of aviation. Pilots rely heavily on the design of cockpit controls, displays, and interfaces to operate aircraft safely and efficiently. By applying Human Factors principles, aviation experts have been able to improve cockpit designs, reducing the likelihood of errors and accidents.
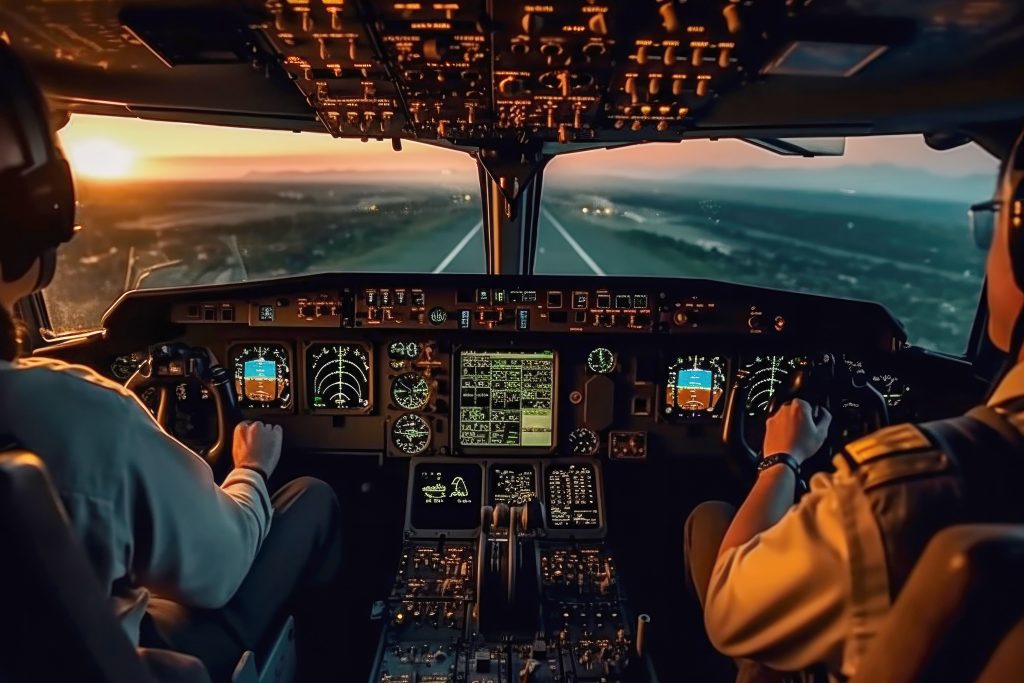

Furthermore, the study of Human Factors is essential in healthcare settings. Medical devices and equipment need to be designed with the user in mind, considering factors such as ease of use, comfort, and safety. By incorporating Human Factors research into the design process, healthcare professionals can ensure that medical devices are intuitive and efficient, ultimately improving patient care.
The Role of Human Factors in Different Industries
Human Factors is a multidisciplinary field that focuses on understanding human capabilities, limitations, and behaviors to optimize the design of systems, products, and environments. This field plays a crucial role in various industries, including healthcare, aviation, and product design.
Human Factors in Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, Human Factors ensures the safe and efficient delivery of medical services. By considering the needs and capabilities of healthcare providers and patients, Human Factors experts design user-friendly medical devices, optimize workflow processes, and create intuitive interfaces. This, in turn, reduces medical errors, improves patient outcomes, and enhances overall healthcare quality. (1)
For example, Human Factors experts analyze the physical and cognitive demands placed on healthcare professionals during various procedures. They identify potential sources of error, such as confusing medication labels or complex medical equipment interfaces, and propose design solutions to mitigate these risks. By incorporating principles of Human Factors into healthcare settings, medical professionals can focus more on patient care and less on navigating complex systems. (2)
Furthermore, Human Factors experts collaborate with healthcare providers to conduct usability testing and gather feedback on medical devices and software. This iterative design process ensures that the technology used in healthcare settings is intuitive, efficient, and meets the unique needs of both healthcare professionals and patients.
Human Factors in Aviation
Aviation heavily relies on Human Factors to enhance safety and optimize pilot performance. By studying human cognition, situational awareness, and decision-making processes, experts develop cockpit designs, training programs, and safety protocols. This results in improved pilot performance, reduced human error, and ultimately, safer air travel for all passengers. (3)
Human Factors experts in aviation focus on understanding how pilots interact with complex flight systems and how they make critical decisions under pressure. They analyze factors such as cockpit layout, control placement, and information display to ensure that pilots can quickly and accurately interpret information and respond effectively in various flight scenarios.
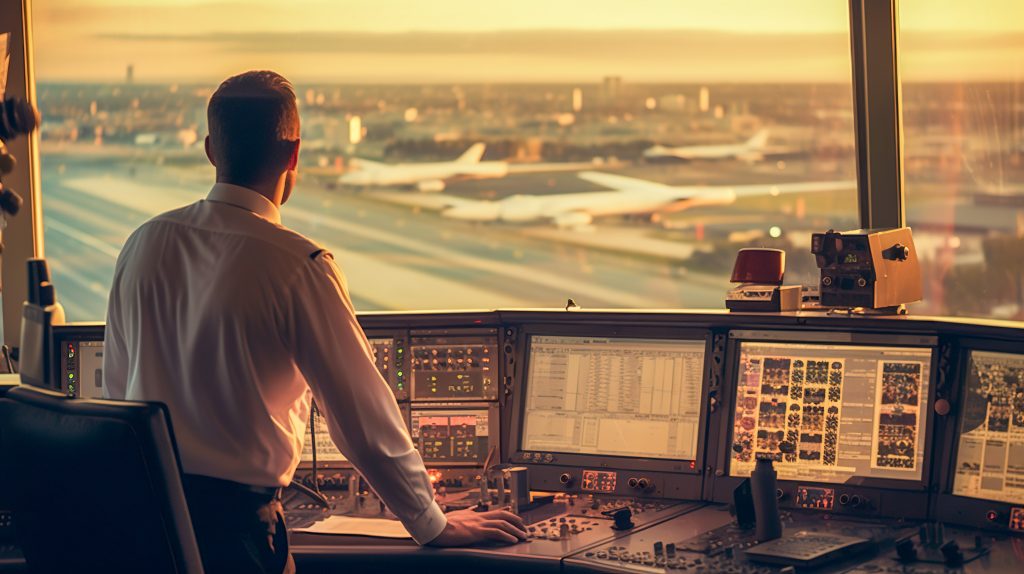

Additionally, Human Factors experts collaborate with aviation training programs to develop realistic simulations and training exercises that replicate real-world scenarios. By incorporating Human Factors principles into pilot training, pilots can develop the necessary skills and decision-making abilities to handle unexpected situations and emergencies.
Human Factors in Product Design
Human Factors plays a fundamental role in product design by ensuring that products are intuitive, comfortable, and safe to use. By considering human anatomy, ergonomics, and user preferences, designers create user-centered products that enhance usability and user satisfaction. From smartphones and furniture to kitchen appliances, Human Factors brings user-centric design to a wide range of products.
Human Factors experts collaborate with designers and engineers to analyze user needs and preferences. They conduct user research, including surveys, interviews, and usability testing, to gather insights into how people interact with products and what design features are most important to them.
For example, in smartphone design, Human Factors experts consider factors such as screen size, button placement, and menu navigation to ensure that users can easily and comfortably interact with the device. They also consider the visual and auditory feedback provided by the device to ensure that users can understand and respond to notifications and alerts. (4)https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0018720818792758
In the furniture industry, Human Factors experts analyze the ergonomics of seating and workspace design to promote comfort and reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. They consider factors such as seat height, backrest support, and adjustability to accommodate a wide range of body types and preferences.
By incorporating Human Factors principles into product design, companies can create products that not only meet functional requirements but also provide an enjoyable and efficient user experience.
Key Principles of Human Factors
Human Factors is a multidisciplinary field that focuses on optimizing the interaction between humans and machines. It encompasses various principles and methodologies to ensure that systems, products, and environments are designed with the user in mind. In this article, we will explore three key principles of Human Factors: the human-machine interface, cognitive ergonomics, and physical ergonomics.
The Human-Machine Interface
The human-machine interface is a crucial element in Human Factors. By designing intuitive interfaces and controls, users can easily interact with complex systems. Human Factors experts incorporate principles of user-centered design, such as logical layout, visual clarity, and feedback mechanisms, to create seamless interactions between humans and machines.

For example, in the design of a smartphone, Human Factors experts consider factors such as the placement of buttons, the size and spacing of icons, and the responsiveness of the touchscreen. By ensuring that these elements are well-designed and user-friendly, they enhance the overall user experience and reduce the risk of errors or frustration.
Cognitive Ergonomics
Cognitive ergonomics focuses on understanding how humans perceive, process, and interpret information. By considering human memory, attention, and decision-making, designers can optimize the presentation and organization of information. This leads to improved comprehension, reduced cognitive load, and more effective decision-making.
One area where cognitive ergonomics plays a significant role is in the design of websites and software interfaces.
Human Factors experts analyze the cognitive processes involved in navigating through information and ensure that the layout, typography, and visual hierarchy are designed to facilitate easy information processing. By reducing cognitive load, users can navigate through the system more efficiently and make informed decisions.
Physical Ergonomics
Physical ergonomics deals with the design of workspaces and equipment to ensure optimal comfort, safety, and efficiency for users. By considering factors such as posture, reachability, and anthropometric measurements, Human Factors experts create ergonomic solutions that minimize physical strain, reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders, and enhance overall productivity.
For example, in the design of office chairs, Human Factors experts consider factors such as lumbar support, adjustable armrests, and seat height. These features are designed to promote proper posture and reduce the risk of back pain or discomfort. Similarly, in the design of manufacturing equipment, Human Factors experts consider the physical movements required by the operators and design the equipment to minimize repetitive strain injuries.

In conclusion, Human Factors is a field that focuses on optimizing the interaction between humans and machines. By incorporating principles of user-centered design, cognitive ergonomics, and physical ergonomics, Human Factors experts create systems, products, and environments that are user-friendly, efficient, and safe. By considering the needs and capabilities of the users, Human Factors helps to improve overall user experience and enhance performance.
Challenges and Solutions in Human Factors
Common Issues in Human Factors
Despite its importance, Human Factors faces various challenges in practice. These challenges include designing for diverse user populations, adapting to technological advancements, and managing time and budget constraints. Additionally, human variability and individual differences must be considered when developing user-centered solutions.
Strategies for Improving Human Factors
To overcome these challenges, organizations can implement strategies to improve Human Factors. These strategies may include involving Human Factors experts from the earliest stages of the design process, conducting usability testing with representative users, and continuously gathering feedback to inform iterative improvements. Collaboration among multidisciplinary teams is also essential for successfully addressing Human Factors challenges.
Utilizing iMotions in Human Factors Research
The iMotions software platform is in many ways created for human factors research, and it stands as a pivotal tool in the field. By allowing for the integration of multiple biosensors and data streams it offers a comprehensive understanding of human factors. This chapter delves into the myriad ways iMotions is employed to enrich research in this domain.
Eye Tracking: A Window to the User’s Focus
A fundamental aspect of iMotions is its support for eye tracking technology. This facet is crucial for ascertaining where participants direct their gaze, the duration of their focus, and the elements that capture their attention. In human factors, such insights are indispensable for evaluating the usability of designs, understanding how users interact with interfaces, and identifying potential safety hazards within physical environments.
Facial Expression Analysis: Decoding Emotional Responses
iMotions excels in analyzing facial expressions to deduce emotional responses. This capability is paramount in assessing user satisfaction, stress levels, and emotional engagement with products or systems. By gauging subtle changes in facial expressions, researchers can infer the emotional impact of a product or interface, providing valuable feedback for design improvements. This analysis is particularly beneficial in scenarios where direct user feedback may be limited or biased.
EEG: Unraveling Cognitive Processes
Another cornerstone of iMotions is its integration with EEG (Electroencephalography), which offers a window into brain activity. This data is instrumental in understanding cognitive workload, attention, and mental states. In the realm of human factors, EEG data plays a critical role in evaluating cognitive ergonomics. It helps ensure that systems and interfaces are designed to facilitate ease of use and avoid unnecessary cognitive strain, thereby enhancing efficiency and user experience.
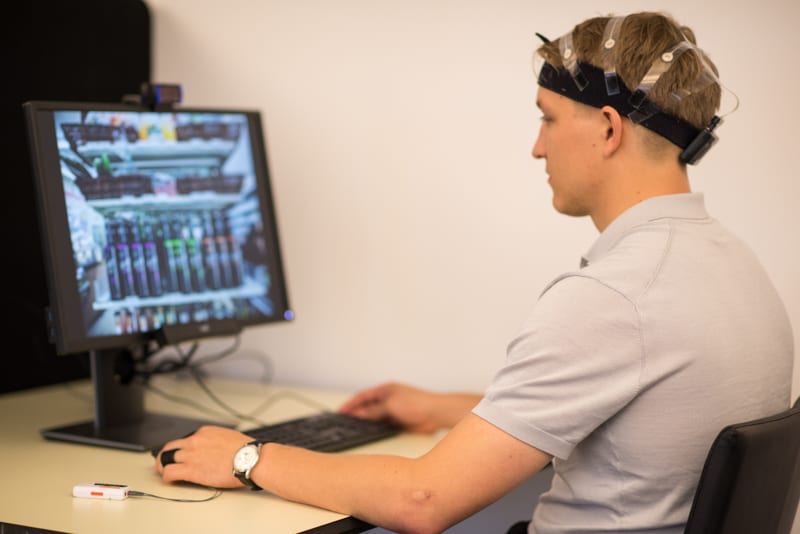

GSR: Measuring Physiological Arousal
The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) feature of iMotions measures sweat gland activity, which correlates with physiological arousal. In human factors research, GSR provides invaluable insights into stress responses, excitement levels, or engagement when individuals interact with different systems or environments. This physiological data complements cognitive and emotional assessments, painting a fuller picture of the user experience.
ECG and HRV: Insights into Cardiovascular Responses
iMotions also encompasses ECG (Electrocardiography) and HRV (Heart Rate Variability) measures, offering insights into the heart’s behavior. These metrics are indicative of stress, workload, and emotional states. In human factors, understanding cardiovascular responses is key for designing environments and systems that are not overly taxing on the user, thereby fostering well-being and productivity.
Synchronizing Multiple Data Streams
A significant advantage of iMotions is its capability to synchronize and analyze data from various sources simultaneously. This holistic approach allows for a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of human responses. It’s especially critical in complex scenarios where multiple aspects of human interaction with systems need to be understood in unison.
Real-Time Data Analysis and Visualization
The platform offers real-time data analysis and visualization tools. This feature is invaluable for obtaining immediate feedback during user testing or experimental trials, enabling researchers and designers to make prompt adjustments and decisions.
Customization and Scalability
iMotions is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it can be tailored to specific research requirements and is scalable to accommodate a range of study sizes. This flexibility makes it suitable for diverse applications, from small-scale usability tests to extensive field studies.
Broad Applications Across Domains
The versatility of iMotions extends across various domains such as automotive design, aviation, healthcare, product design, and workplace safety. In each of these fields, understanding human factors is essential for optimizing efficiency, ensuring safety, and enhancing user satisfaction.
Future Trends in Human Factors
The Impact of Technology on Human Factors
As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented rate, Human Factors will play an increasingly important role. Emerging technologies such as virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and smart devices will require careful consideration of human factors to ensure optimal user experience, safety, and ethical design. Integrating Human Factors into the development of these technologies will be crucial for successfully adapting to the future.
The Role of Human Factors in Sustainable Development
Human Factors also intersects with sustainable development goals. By considering human behavior, environmental impact, and social factors, Human Factors experts can help design sustainable systems and products that minimize resource consumption, reduce waste generation, and promote a more sustainable way of living. This interdisciplinary approach can have a profound impact on shaping a greener future.
Human Factors is a multidisciplinary field that considers human capabilities, limitations, and behaviors to optimize the design and function of systems across various industries. By understanding the definition, importance, and role of Human Factors, along with key principles, challenges, and future trends, we can better appreciate its impact on performance, safety, and user experience. As technology progresses and new challenges arise, the field of Human Factors will continue to evolve, creating a more user-friendly, efficient, and sustainable world.
Frequently Asked Questions About Human Factors
What is the main goal of human factors research?
The primary goal is to optimize human interaction with systems to improve safety, efficiency, and user experience.
How does human factors differ from ergonomics?
While human factors focus on psychological and cognitive aspects, ergonomics emphasizes physical comfort and efficiency.
What industries use human factors research?
Human factors are used in aviation, healthcare, automotive design, UX design, workplace safety, and many more.
Why is human factors important in UX design?
Human factors ensure that websites, apps, and software are intuitive, reducing frustration and enhancing usability.
How can businesses benefit from human factors research?
Companies that apply human factors principles reduce errors, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance product usability.
References
1: Carayon P, Xie A, Kianfar S., Human factors and ergonomics as a patient safety practice. BMJ Quality & Safety 2014;23:196-205. https://qualitysafety.bmj.com/content/23/3/196
2: Purchase, T., Bowie, P., Hibbert, P., Krishnan, R.G., Carson-Stevens, A. (2023). Human Factors to Improve Patient Safety. In: Agrawal, A., Bhatt, J. (eds) Patient Safety. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35933-0_4
3: Chan WT, Li WC. Development of effective human factors interventions for aviation safety management. Front Public Health. 2023 May 5;11:1144921. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1144921. PMID: 37213611; PMCID: PMC10196386.
4: Lee, S., Kyung, G., Yi, J., Choi, D., Park, S., Choi, B., & Lee, S. (2019). Determining Ergonomic Smartphone Forms With High Grip Comfort and Attractive Design. Human Factors, 61(1), 90-104. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018720818792758