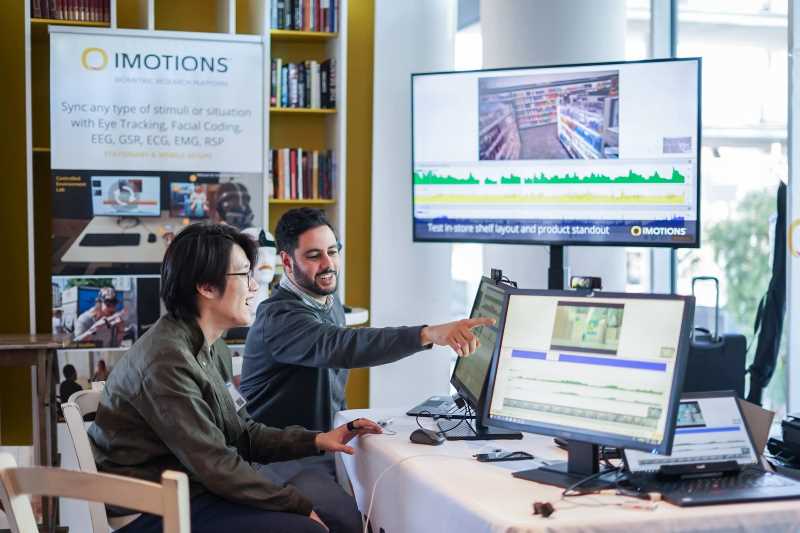
Mediators aim to shape group dynamics in various ways, such as improving trust and cohesion, balancing participation, and promoting constructive conflict resolution. Technological systems used to mediate human-human interactions must be able to continuously assess the state of the interaction and generate appropriate actions. In this paper, behavioral cues that indicate interpersonal perception in dyadic social interactions are investigated. These cues may be used by such systems to produce effective mediation strategies. These are used to evaluate dyadic interactions, in which each interactant rates how agreeable or disagreeable the other interactant comes across. A multi-perspective approach is taken to evaluate interpersonal affect in dyadic interactions, employing computational models to investigate behavioral cues that reflect interpersonal perception in both the interactant providing the rating and the interactant being rated. The findings offer nuanced insights into interpersonal dynamics, which will be beneficial for future work on technology-assisted social mediation.