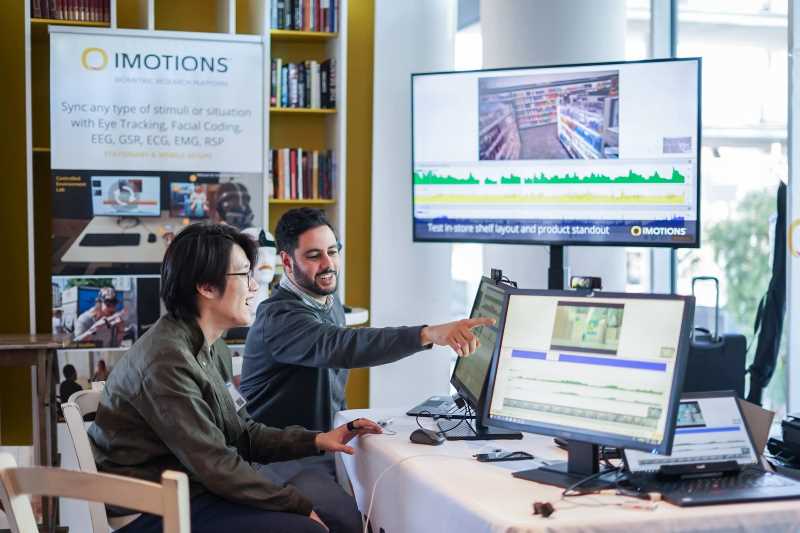
Current research on personalized learning paths based on artificial intelligence (AI) generally has black-box problems. It relies more on learning behavior data and lacks real-time monitoring of learners’ physiological states, leading to delayed personalized adjustments, lack of explainability of decision-making logic, and difficulty in gaining the trust of educators and learners. This paper integrates multimodal biometric identification and analysis (MM-BIA) technology and an explainable AI algorithm to construct a dynamic path optimization framework that conforms to educational principles. This paper uses the Tobii Pro Nano eye tracker to collect data, synchronizes it through the iMotions platform, and calculates indicators such as gaze duration and saccade speed. Dlib is used to locate facial features, and the ResNet-18 (Residual Network-18) model technology is used for micro-expression recognition. Combining electroencephalography (EEG) signals with the entropy of the mouse trajectory, a regression model is constructed using XGBoost (eXtreme Gradient Boosting) to evaluate feature importance. The results show that this paper’s multi-stage signal processing pipeline of Kalman filtering, wavelet denoising, and morphological processing improves the signal-to-noise ratio of eye movement signals from 2.0 to 6.1. MM-BIA performs well in many aspects, with an accuracy of 0.936, higher than the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)-Transformer’s 0.721. Its F1-score is 0.916, higher than the Light Vision Transformer (LightViT)’s 0.772. The inference delay is 38ms, lower than the 210ms of the Multimodal-Large Language Model (LLM). This study integrates multimodal biometric identification technology and explainable AI algorithms to construct personalized learning paths, breaking the limitations of traditional learning path construction, promoting the cross-integration of instructional technology, cognitive science, and AI, and providing key support for the development of intelligent education, the digital realization of “teaching. students in accordance with their aptitude”, and the construction of AI credibility in education.