Fragrance testing explores how scents influence human behavior by evaluating their emotional, cognitive, and sensory impacts. From natural and synthetic components to psychological responses, this field blends chemistry and psychology to reveal how fragrances affect mood, memory, and decision-making, providing insights for marketing, therapy, and environmental design.
Table of Contents
In the countless influences that constitute the “human experience”, fragrance holds a unique place. From the earliest civilizations all the way up to modern societies, scents have been revered for their power to evoke memories, influence emotions, enhance well-being and create atmosphere in any setting.

The art and science of creating fragrances have evolved over millennia, leading to the sophisticated and diverse array of aromas that we covet today. At the heart of this olfactory landscape and the quest for understanding human behavior we have fragrance testing-a field where chemistry, psychology, and sensory science come together to untangle the intricacies of how scent influences the human psyche, our emotions, and our actions.
Fragrance testing is, at its core, an endeavor to systematically evaluate and understand the characteristics of scents and their impact on people. This process encompasses a wide range of methodologies, from the analysis of fragrance composition to the assessment of emotional and cognitive responses elicited by specific scents. The ultimate objective is not just to refine the sensory appeal of fragrances but to delve deeper into how they can modify mood, memory, decision-making, and overall behavior.
The relationship between fragrances and human behavior is a rich field of inquiry that offers fascinating insights into the human mind. It raises intriguing questions about the nature of perception and the unseen forces that shape our experiences and interactions.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of fragrance testing and its significance in human behavior research. Through an exploration of scientific studies, methodological approaches, and the ethical considerations involved, we will illuminate the multifaceted ways in which scents influence our lives, both overtly and subtly.
Section 1: The Science of Fragrance
The allure of fragrance is rooted in its complex chemistry and the intricate way in which humans perceive and process these olfactory signals. Understanding the science of fragrance is essential to appreciate its impact on human behavior and the methodologies behind fragrance testing.
Composition of Fragrances: Natural vs. Synthetic Components
Fragrances are composed of volatile chemicals that evaporate into the air, allowing their scent to be detected by the human nose. These compounds can be sourced from natural materials such as flowers, fruits, woods, and resins, or synthesized in laboratories to create a vast array of scents.
Natural components, like essential oils extracted from plants, have been used since ancient times and are valued for their complexity and depth. Synthetic ingredients, on the other hand, offer consistency, sustainability, and the ability to create novel scents not found in nature.
How Fragrances Are Detected and Processed by the Human Olfactory System
The perception of fragrance begins when odor molecules bind to receptors in the olfactory epithelium, a small patch of tissue at the back of the nasal cavity. This interaction generates a signal that is transmitted to the olfactory bulb and then to various regions of the brain, including those responsible for emotion, memory, and decision-making.
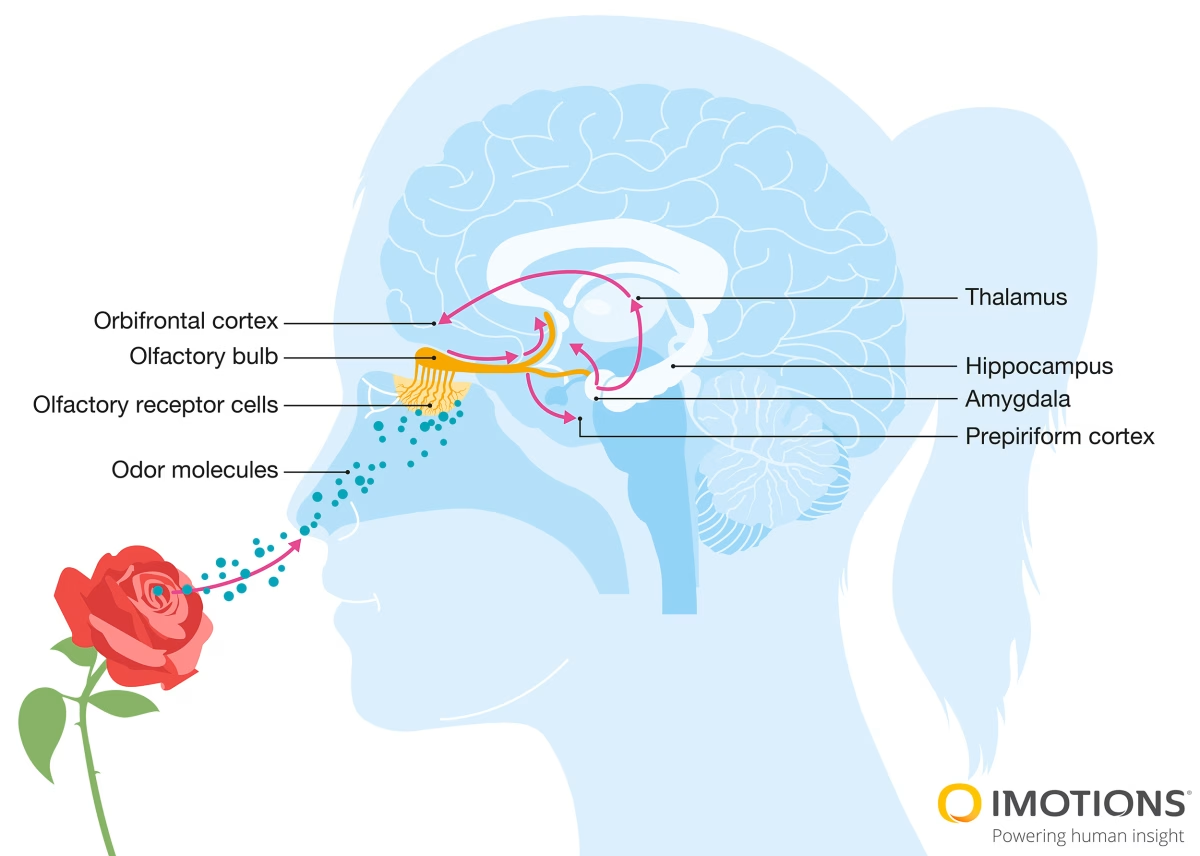
The human olfactory system can distinguish thousands of different scents, a testament to the complexity and sensitivity of our sensory processing capabilities. This process is central to understanding the psychological and emotional effects fragrances can have on individuals .
Psychological and Emotional Effects of Fragrances on the Human Brain
The impact of fragrances on the brain is profound and multifaceted. Scents can trigger memories, influence mood, and even affect cognitive functions. For example, the smell of lavender is often associated with relaxation and has been shown to decrease stress levels in various settings .
Conversely, the scent of citrus can invigorate and enhance alertness. These effects are thought to arise from the direct pathways between the olfactory system and the limbic system, the brain’s emotional center. Understanding these interactions is crucial for the application of fragrance in areas such as aromatherapy, product design, and environmental engineering to elicit desired responses from individuals.
Section 2: Fragrance Testing Methodologies
To fully understand the impact of fragrances on human behavior, researchers employ various testing methodologies. These approaches range from analytical chemistry techniques to sensory evaluation methods, each offering unique insights into the characteristics and effects of fragrances.
Overview of Common Methods Used in Fragrance Testing
Fragrance testing methodologies can be broadly categorized into two main types: analytical and sensory. Analytical methods, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), allow scientists to identify and quantify the chemical components of a fragrance. This technique is crucial for understanding the composition of a scent and ensuring its consistency and safety.
On the other hand, sensory evaluation involves human participants and focuses on the perceptual attributes of fragrances. Methods such as hedonic rating scales and forced-choice tests are used to assess preferences, intensity, and other qualitative aspects of a scent .
The Role of Human Subjects in Fragrance Testing
Human subjects are integral to fragrance testing, providing subjective data on the sensory experience of a scent – after all, we are the ones who smell it. This information is essential for understanding the emotional and behavioral effects of fragrances. The use of human panels allows researchers to gather data on preference, detectability, and the ability of a fragrance to evoke specific memories or emotions.
Advancements in Technology and Their Impact on Fragrance Testing Methods
Technological advancements have significantly impacted fragrance testing methodologies. For example, electronic noses (e-noses), devices that mimic the human olfactory system, offer new ways to analyze and classify fragrances. These instruments can provide rapid, objective data on scent profiles, complementing the subjective assessments obtained from human panels.
Additionally, virtual reality (VR) technology has emerged as a tool for simulating environments and contexts in which fragrances are experienced, allowing researchers to study the effects of scents in controlled yet realistic settings.
Fragrance Testing and Human Behavior Research
The study of fragrance and its influence on human behavior reveals a fascinating and complex relationship between scent and our emotional, cognitive, and physiological states. Fragrances have the ability to alter mood, enhance memory, and even affect decision-making. Modern fragrance testing brings together disciplines such as sensory science, psychology, and neuroscience to explore how different scents impact the brain and behavior, from reducing stress to promoting alertness.
The Role of GSR and EEG in Fragrance Testing with iMotions
iMotions is at the forefront of fragrance testing by providing advanced tools for analyzing the physiological and neurological effects of scent. Two key technologies-Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Electroencephalography (EEG)-are particularly useful in this field. GSR measures changes in skin conductance, offering real-time data on emotional arousal when participants are exposed to specific fragrances. This helps researchers understand whether a scent induces relaxation, excitement, or stress.

EEG, on the other hand, measures brain activity and can provide insights into cognitive responses to fragrances. It helps determine whether a scent enhances focus, promotes relaxation, or triggers specific memories. By using EEG, researchers can also analyze how different regions of the brain react to various olfactory stimuli, offering a deeper understanding of the neural processes behind scent perception.
Impact Across Industries
The application of iMotions’ technology within fragrance testing extends beyond personal care and into fields like marketing, product design, and environmental engineering. By leveraging biosensor technology, companies can refine their fragrance offerings to optimize customer experiences, enhance well-being, or create targeted olfactory environments that improve productivity or relaxation. These biometric tools provide actionable insights, allowing businesses to design scent strategies that are scientifically proven to influence behavior, improve mental health, or elevate brand perception.
Free 59-page EEG Guide
For Beginners and Intermediates
- Get a thorough understanding of the essentials
- Valuable EEG research insight
- Learn how to take your research to the next level











